Understanding the Four C's of Diamonds: A Guide on How to Buy Natural Diamonds
- innayajewelry.hs

- Jan 16, 2025
- 2 min read
When it comes to purchasing a diamond, whether for an engagement ring, a gift, or a personal treat, understanding the Four C's is essential. These four characteristics—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight—play a significant role in determining a diamond’s beauty and value. In this blog post, we'll explore each of these attributes in detail, helping you make an informed decision for your next diamond purchase.
1. Cut
The cut of a diamond is perhaps the most crucial factor influencing its overall appearance. It refers not just to the shape of the diamond (like round, princess, or oval) but also to how well it has been crafted. A well-cut diamond will reflect light beautifully, displaying brilliance and sparkle.
Key Points:
Brilliance: The amount of light a diamond reflects.
Proportions: The angles and dimensions that affect how light travels through the diamond.
Grades: Cut grades range from Excellent to Poor. Higher grades mean better craftsmanship and light performance.

2. Color
Diamonds come in a variety of colors, but the most valued diamonds are those that are colorless or near-colorless. The Gemological Institute of America (GIA) grades diamond color on a scale from D (colorless) to Z (light yellow or brown).
Key Points:
Colorless diamonds (D-F) are the rarest and most desirable.
Near-colorless diamonds (G-J) still appear mostly colorless to the naked eye and offer a great value.
Fancy colors: Diamonds can also come in hues like pink, blue, and yellow, which can significantly affect price and desirability.

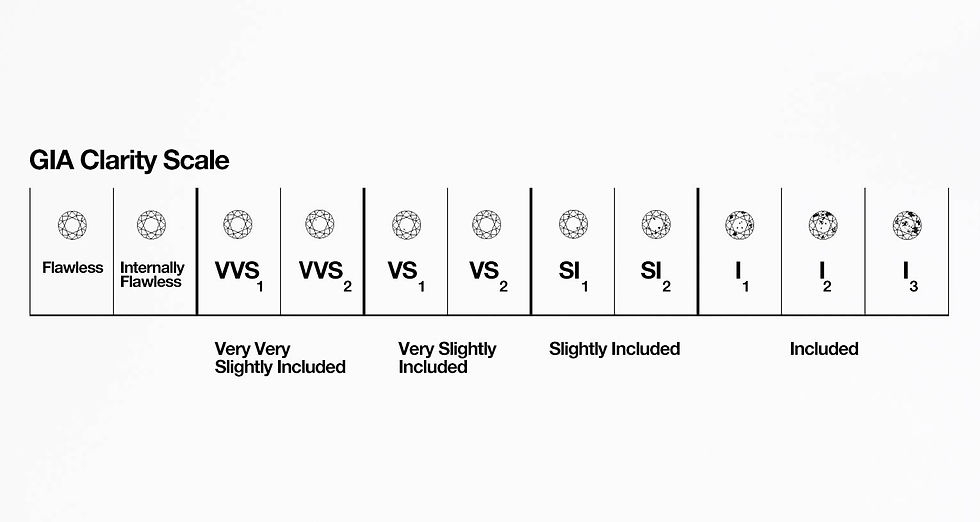
3. Clarity
Clarity measures the presence of internal or external flaws, known as inclusions and blemishes. The fewer imperfections a diamond has, the higher its clarity grade. Clarity is graded on a scale from Flawless (no inclusions visible under 10x magnification) to Included (inclusions visible to the naked eye).
Key Points:
Flawless (F): No inclusions, very rare.
Internally Flawless (IF): No inclusions visible under 10x magnification, but may have minor surface blemishes.
VS1-VS2: Very Slightly Included; inclusions are difficult to see.
SI1-SI2: Slightly Included; inclusions may be visible to a trained eye.
I1-I3: Included; inclusions are visible to the naked eye.
4. Carat Weight
Carat weight measures the size of the diamond. One carat is equivalent to 200 milligrams. While larger diamonds are generally more valuable, the relationship between carat weight and value is not linear. A diamond’s price increases significantly with each additional carat.
Key Points:
Size vs. Value: A one-carat diamond can be much more expensive than a 0.90-carat diamond due to the rarity of larger stones.
Visual Size: Factors like cut and shape can influence how large a diamond appears, so it’s important to consider these alongside carat weight.

Understanding the Four C's of Diamonds—Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat weight—empowers you to make informed choices when shopping for diamonds. Whether you're looking for a stunning engagement ring or a unique piece of jewelry, knowing these characteristics will help you select a diamond that meets your aesthetic and budgetary needs.
Happy diamond hunting! If you have any questions or need assistance, feel free to reach out. We’re here to help you find the perfect diamond at Innaya Jewelry/Argo Diam, in Hong Kong, NYC, Shanghai and Mumbai.




Comments